In the world of virtualization, the term hypervisor often comes up. It might sound like a fancy buzzword, but the concept is simple. A hypervisor is the technology that makes it possible to run multiple operating systems (OS) on a single physical machine.
In this article, we’ll break down what a hypervisor is, how it works, and the two main types you’ll come across.
Table of Contents
What is a Hypervisor?
A hypervisor is software (or firmware) that creates and runs virtual machines (VMs). Think of it as a resource manager that collects hardware resources like:
- CPU
- Memory
- Storage
- Network
It then pools these resources and distributes them to VMs as needed.
- The physical machine that runs the hypervisor is called the Host.
- The virtual machines running on top are called Guests.
With a hypervisor, you can run multiple operating systems simultaneously on the same hardware, making your system more efficient.
Types of Hypervisors
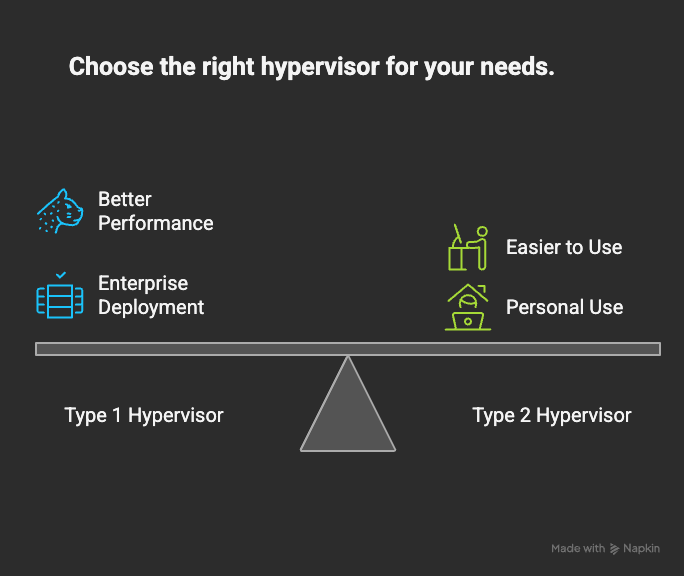
Type 1 Hypervisor (Bare-Metal Hypervisor)
- Runs directly on the host hardware without a traditional operating system.
- Provides better performance and efficiency.
- Commonly used in enterprise and data centers.
Examples:
- VMware vSphere/ESXi
- Microsoft Hyper-V
- KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine)
Type 2 Hypervisor (Hosted Hypervisor)
- Runs on top of a host operating system (like Windows, Linux, or macOS).
- Easier to install and use but slightly slower than Type 1 due to the extra OS layer.
- Ideal for personal use, testing, and development.
Examples:
- Oracle VirtualBox
- VMware Workstation
- Parallels Desktop
FAQs About Hypervisors
A hypervisor is software that lets you run multiple operating systems on a single computer.
They allow better resource utilization, flexibility, and cost savings by running multiple VMs on the same hardware.
Type 1 runs directly on hardware (faster, enterprise use). Type 2 runs on top of an OS (slightly slower, personal use).
Yes! Type 2 hypervisors like VirtualBox and VMware Workstation can run on regular desktops and laptops.
Type 1 hypervisors like VMware ESXi, Hyper-V, or KVM are preferred in enterprise environments.
Conclusion
A hypervisor is the backbone of virtualization. By acting as a bridge between hardware and virtual machines, it enables you to run multiple OS on the same computer, use resources more efficiently, and cut costs.
- Use Type 1 hypervisors if you need enterprise-grade performance and scalability.
- Use Type 2 hypervisors if you just want to test, learn, or run different OS on your personal machine.
In short: Hypervisors make virtualization possible—and virtualization makes modern IT smarter, faster, and more efficient.






[…] – The virtualize software download from the below […]
[…] – Oracle VM VirtualBox is a type-2 hypervisor for x86 virtualization developed by Oracle Corporation. You can download the VirtualBox from […]