In a virtualized environment, networking plays a critical role in enabling seamless communication between virtual machines (VMs) and the physical network. This is where a vSwitch in VMware — also known as a virtual switch — comes into play.
A vSwitch is a software-based networking component that connects virtual machines, hosts, and external networks. It functions just like a physical switch, forwarding data packets based on MAC addresses, but operates entirely within the hypervisor layer.
If you’re managing VMware vSphere or ESXi, understanding how a vSwitch in VMware works is essential for configuring virtual networks effectively.
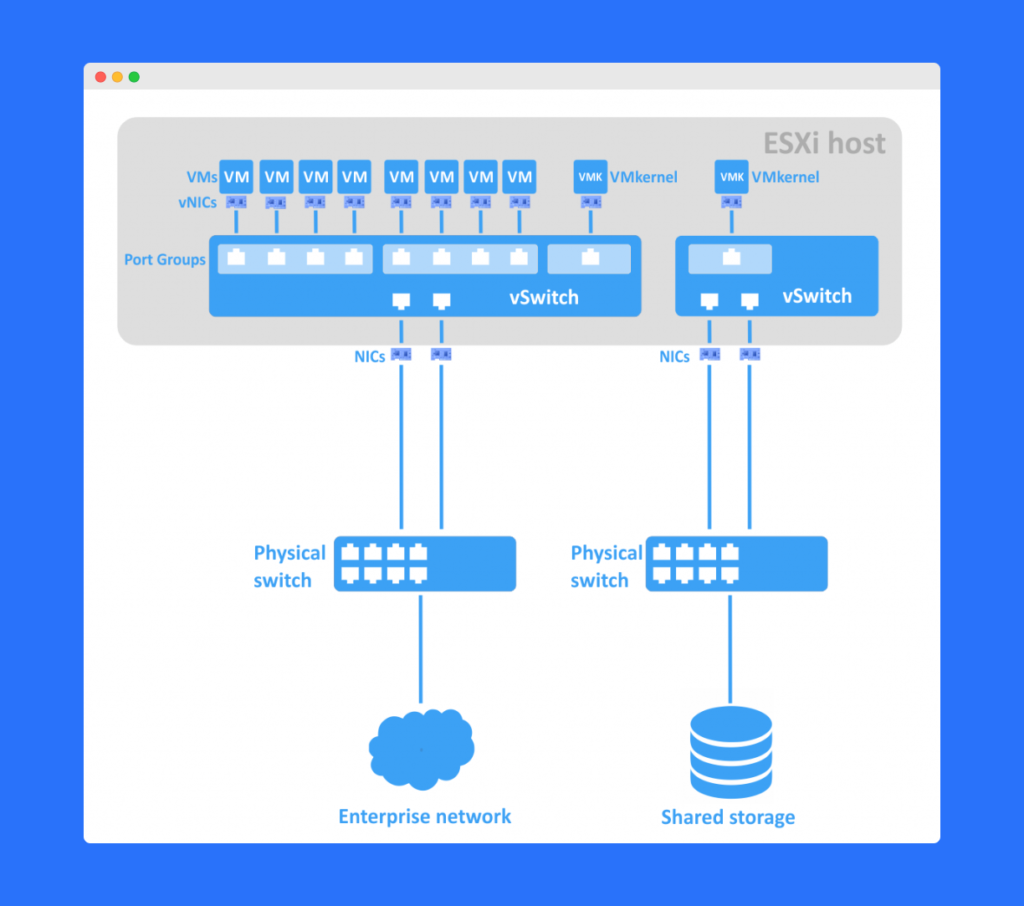
Table of Contents
What Is a vSwitch (Virtual Switch)?
A vSwitch (virtual switch) is a logical representation of a physical network switch. It manages network traffic within the virtualized environment by connecting:
- Virtual Machines (VMs)
- Virtual Network Interface Cards (vNICs)
- Physical network adapters (pNICs)
Each vSwitch can contain multiple virtual ports, and each port connects to a vNIC. These vNICs belong to virtual machines or other virtual devices.
Essentially, a vSwitch enables VMs to communicate internally within the same host or externally with the physical network.
Key Components of a vSwitch in VMware
To better understand how a vSwitch operates, let’s break down its main components:
Virtual Network Interface Cards (vNICs)
Each virtual machine is assigned one or more vNICs. These act as the virtual equivalent of physical network cards, allowing the VM to send and receive data through the vSwitch.
Virtual Port Groups (VPGs)
A Virtual Port Group (VPG) is a logical grouping of vNICs that share the same network policies and settings.
For example, VPGs can be used to:
- Group VMs belonging to the same department or subnet.
- Apply security policies, VLAN IDs, or Quality of Service (QoS) configurations.
Uplinks (Physical NICs or pNICs)
A vSwitch connects to physical network adapters known as uplinks. These uplinks enable traffic from virtual networks to reach external networks.
Virtual Switch Policies
Administrators can configure policies for:
- Security (MAC address changes, forged transmits)
- Traffic shaping (bandwidth control)
- Load balancing and failover
How Does a vSwitch in VMware Work?
To understand a vSwitch’s functionality, imagine how a physical network switch operates.
A physical switch receives incoming packets on one port and forwards them to another based on the destination MAC address.
A vSwitch in VMware behaves the same way, but in software form:
- The vSwitch receives a packet from a virtual NIC (vNIC).
- It checks the destination MAC address.
- If the destination vNIC exists within the same virtual network, the vSwitch sends the packet internally.
- If the destination is external, it forwards the packet through the physical uplink to the external network.
This process enables efficient communication between VMs, even across different hosts, without the need for physical switches to handle all the internal traffic.
Types of vSwitches in VMware
VMware offers two main types of virtual switches:
Standard vSwitch (vSS)
- Configured individually on each ESXi host.
- Ideal for smaller environments.
- Basic networking features such as VLANs and NIC teaming.
Distributed vSwitch (vDS)
- Managed centrally via vCenter Server.
- Offers advanced features like Network I/O Control (NIOC) and centralized policy management.
- Best suited for large-scale enterprise environments.
Benefits of Using a vSwitch in VMware
A vSwitch in VMware offers multiple benefits that enhance both performance and security:
- Improved Network Isolation: Segregate traffic using VLANs.
- Simplified Management: Create logical groupings of virtual networks.
- Scalability: Easily scale virtual networks without new hardware.
- Performance Optimization: Manage traffic shaping and load balancing.
- Automation Ready: Integrates seamlessly with VMware vCenter and other automation tools.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A vSwitch in VMware connects virtual machines and other virtual devices to each other and to physical networks, managing data traffic efficiently.
VMware provides two types: the Standard vSwitch (vSS) for single-host setups and the Distributed vSwitch (vDS) for centralized management across multiple hosts.
A vSwitch works like a physical switch, forwarding packets based on MAC addresses between virtual NICs and uplinks.
A VPG is a logical group of vNICs with shared network settings, used to apply consistent policies such as VLAN tagging or QoS rules.
A vSwitch in VMware enables efficient communication, network segmentation, and management across virtualized environments, making it essential for performance and scalability.
Conclusion
A vSwitch in VMware is a powerful virtual networking component that replicates the functions of a physical switch — without requiring additional hardware.
By enabling communication between virtual machines, hosts, and external networks, a vSwitch ensures smooth and efficient traffic flow within virtualized environments.
Whether you’re managing a small VMware setup or a large-scale data center, understanding how a vSwitch works helps you build secure, scalable, and optimized virtual networks.





