In today’s IT world, storage is one of the most valuable resources. You’ve probably heard people say things like “We need to provision more storage for this server” or “The provisioned space is almost full.” But what exactly does storage provisioning mean?
Don’t worry—this article breaks it down with simple examples so you can clearly understand what it is and how it’s used in businesses.
Table of Contents
What is Storage Provisioning?
Storage provisioning is the process of assigning storage space from a storage system (like a SAN – Storage Area Network) to devices such as servers, virtual machines, or applications.
It can be done automatically or manually by a storage administrator.
Simple Example
Imagine your company has a 10 TB SAN:
- You need 10 virtual machines (VMs) for your employees.
- Each VM is assigned 512 GB, totaling around 5 TB.
- You also create a 3 TB shared storage for projects.
Now you’ve used about 8 TB, leaving 2 TB for future use. This step-by-step allocation is what we call storage provisioning.
Types of Storage Provisioning
There are mainly two approaches:
- Thick Provisioning
- Thin Provisioning
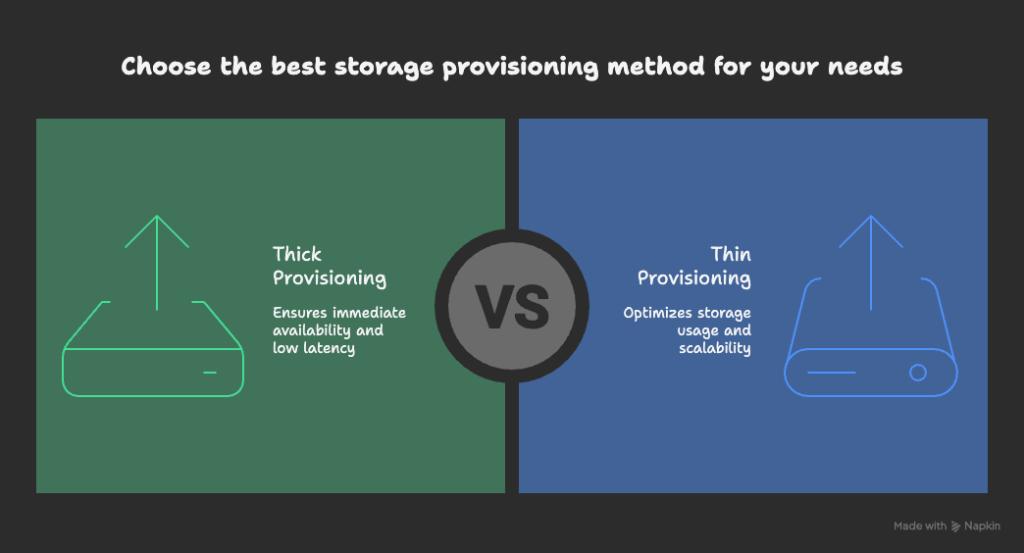
Thick Provisioning
In thick provisioning, you assign the full amount of storage upfront. For example, if you create a 3 TB share, the system immediately reserves 3 TB for it—no one else can use that space, even if it’s empty.
✅ Benefits:
- Low latency (storage is ready right away).
- Less monitoring needed (space is fixed).
❌ Downsides:
- Costly, because you need all the storage available upfront.
- Can lead to unused storage sitting idle.
Thin Provisioning
In thin provisioning, storage is allocated on demand. If you create a 3 TB share, the system doesn’t immediately reserve the full 3 TB. Instead, it grows as data is added, making more efficient use of available space.
✅ Benefits:
- Reduces wasted storage.
- Scales as your actual usage grows.
❌ Downsides:
- Requires constant monitoring.
- If storage runs out, systems may crash or shut down.
Conclusion
Storage provisioning is a smart way to manage storage resources in IT. With thick provisioning, you reserve space upfront for reliability, while thin provisioning helps save costs by allocating storage only as needed.
Choosing between the two depends on your priorities:
- Pick thick provisioning if you value performance and predictability.
- Choose thin provisioning if flexibility and efficient usage are more important.
By understanding these two methods, you can ensure your company’s storage stays efficient, cost-effective, and ready for growth.