In modern virtualization, efficient network management is crucial. One of the key components enabling this efficiency is the Virtual Port Group (VPG) in VMware.
A Virtual Port Group in VMware is a logical grouping of virtual network interfaces (vNICs) that share the same network properties and configurations. It simplifies how administrators organize virtual machines (VMs), apply security rules, and manage traffic within virtualized environments like VMware vSphere.
Table of Contents
What Is a Virtual Port Group (VPG)?
A Virtual Port Group (VPG) acts as a bridge between virtual machines and the underlying virtual switch (vSwitch). It defines how virtual network interfaces communicate within a network and determines key settings such as VLAN IDs, security policies, and traffic shaping rules.
Each VPG contains multiple vNICs, and these interfaces can belong to different virtual machines but share the same network configurations.
For instance, you might create separate VPGs for production, testing, and management networks — each with its own VLAN and security policies.
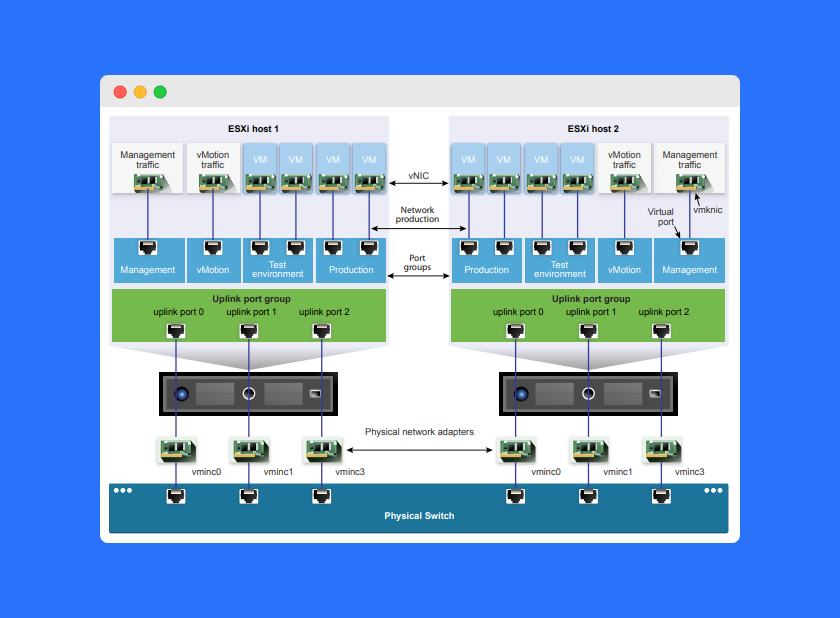
How to Create a Virtual Port Group in VMware
Creating and managing VPGs is straightforward using the VMware vSphere Client (GUI). Here’s how:
- Open the vSphere Client and log in.
- Navigate to the desired vSwitch (virtual switch).
- Click “Add Port Group” to create a new VPG.
- Specify details like the name, VLAN ID, and other networking settings.
- Assign vNICs from virtual machines to this port group.
Once created, the Virtual Port Group in VMware allows all assigned VMs to communicate using the same networking rules and VLAN configuration.
Benefits of Using a Virtual Port Group in VMware
Using VPGs in a VMware environment provides multiple operational and security advantages.
Enhanced Flexibility
Virtual Port Groups offer a scalable and adaptable way to manage network configurations. You can easily add or remove vNICs, update VLAN IDs, or apply specific network policies without disrupting other systems.
Improved Efficiency
VPGs streamline data flow between virtual machines and physical networks, reducing network overhead and improving communication speed across the virtual infrastructure.
Stronger Security
Administrators can apply security policies such as Access Control Lists (ACLs) or VLAN segmentation to prevent unauthorized access and isolate traffic between departments or workloads.
Quality of Service (QoS) Management
With QoS settings, you can prioritize critical applications to ensure they receive adequate bandwidth and stable performance even during network congestion.
How a Virtual Port Group Works
To understand how a Virtual Port Group in VMware operates, it helps to compare it to a physical network switch.
A physical switch connects multiple devices on a network, forwarding data packets based on MAC addresses. It receives packets on one port and sends them out through another port to reach the correct destination.
A Virtual Port Group works similarly but entirely in software:
- It receives packets from one virtual NIC (vNIC).
- It determines the correct destination vNIC based on MAC addresses.
- It forwards the data internally within the host or through the vSwitch to the physical network.
This process allows virtual machines connected to the same VPG to communicate efficiently while maintaining isolation from other network groups.
Best Practices for Managing Virtual Port Groups
To optimize your Virtual Port Group configuration, consider these best practices:
- Use meaningful names for each VPG (e.g., “Prod_Network,” “Test_VMs”).
- Apply VLAN IDs for proper network segmentation.
- Implement security policies like MAC address changes and forged transmit prevention.
- Monitor traffic regularly to ensure network performance and QoS compliance.
- Document configurations for better management and troubleshooting.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A Virtual Port Group in VMware is a logical grouping of vNICs that share the same network configurations, such as VLAN IDs and security policies.
VPGs simplify network management, improve efficiency, and enhance security by applying common networking rules across multiple virtual machines.
You can create a VPG using the vSphere Client by selecting the vSwitch, adding a port group, and defining properties like VLAN ID and name.
Yes, multiple virtual machines can connect to the same Virtual Port Group as long as they share similar network configurations.
A vSwitch acts as the virtual network’s backbone, while a Virtual Port Group defines the policies and configurations applied to VMs connected through that switch.
Conclusion
A Virtual Port Group in VMware is essential for organizing, securing, and managing virtual networks efficiently. It allows administrators to group virtual NICs logically, apply consistent network settings, and ensure smooth communication across the virtual infrastructure.
By mastering VPGs, you’ll be able to build scalable, secure, and high-performing virtual networks that align with business and operational needs.





