A Kubernetes Deployment is a powerful controller that helps manage application workloads. While a ReplicaSet ensures multiple Pods are running, a Deployment manages ReplicaSets themselves, providing scalability, availability, and automation.
In simple terms:
- Kubernetes Deployment → manages ReplicaSets
- ReplicaSet → manages Pods
- Pod → runs containers
This layered structure ensures that if one ReplicaSet fails, another takes over — guaranteeing high availability of your application.
Table of Contents
Advantages of Deployment
It provides several key benefits:
- ✅ High Availability (HA): Keeps your application running during failures.
- ✅ Seamless Upgrades: Roll out new versions without downtime.
- ✅ Automation: Handles scaling, self-healing, and updates automatically.
- ✅ Rollback Support: Quickly revert to a stable version if needed.
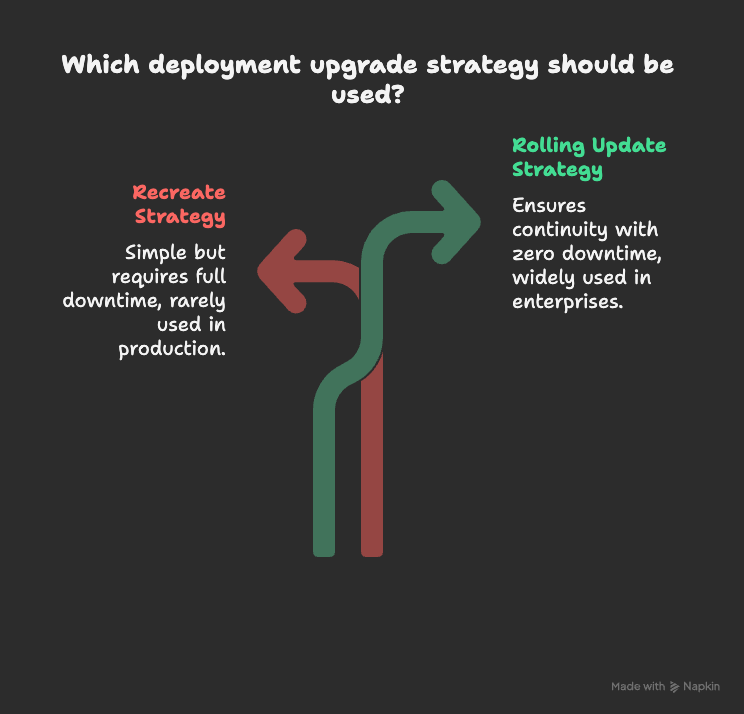
Types of Deployment Upgrades
When updating applications, Kubernetes offers two upgrade strategies within Deployments:
Recreate Strategy
- Stops all Pods, then deploys new ones.
- Simple, but requires full downtime.
- Rarely used in production.
Rolling Update (Default)
- Updates Pods one at a time, ensuring continuity.
- Provides zero downtime upgrades.
- Most enterprises rely on this strategy.
👉 By default, every Deployment uses a rolling update strategy.
How to Create a Deployment YAML File
A Deployment in Kubernetes is usually defined using a YAML file. Here’s a simple example:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: myapp-deployment
labels:
app: nginx
type: frontend
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: myapp
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: myapp
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginxExplanation of the YAML File
- apiVersion: API version in use.
- kind: Specifies
Deployment. - metadata: Deployment name and labels.
- replicas: Number of Pods (3).
- selector: Matches Pods with specific labels.
- template: Defines Pod configuration, including container image.
This YAML creates a Kubernetes Deployment named myapp-deployment with three replicas of Nginx.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
It is used to manage ReplicaSets and Pods, ensuring applications are scalable and always available.
A ReplicaSet manages Pods, while a Kubernetes Deployment manages ReplicaSets and provides upgrade/rollback features.
The Rolling Update strategy is best as it ensures zero downtime.
Yes, Kubernetes allows rolling back to a previous stable Deployment version.
You can scale by editing the replicas value in the YAML file or running kubectl scale deployment myapp-deployment --replicas=5.
Conclusion
A Kubernetes Deployment is essential for managing applications with ease. It simplifies scaling, ensures high availability, and provides smooth updates without downtime. Whether you use Recreate or Rolling Update, Deployments make managing workloads much more efficient.
👉 Try creating your own Kubernetes Deployment YAML and experiment with different upgrade strategies.





