In virtualization, networking plays a vital role in how virtual machines (VMs) communicate with each other and external networks. One essential component that enables this communication is the vNIC in VMware, also known as a Virtual Network Interface Card.
A vNIC is a software-based version of a physical network adapter. It allows VMs and virtual devices to send and receive data just like physical machines — but entirely within the virtualized infrastructure.
Let’s explore what a vNIC in VMware is, how it works, and why it’s a key element in building efficient and secure virtual networks.
Table of Contents
What Is a vNIC (Virtual Network Interface Card)?
A vNIC is a logical representation of a physical network interface card (NIC). It performs the same basic function — enabling network communication — but exists as a software component managed within the VMware vSphere environment.
Each vNIC connects to a virtual switch (vSwitch), which is responsible for directing traffic between VMs or between a VM and the physical network.
By using vNICs, you can:
- Create virtual networks without additional hardware.
- Control network performance.
- Apply consistent network and security policies.
This makes the vNIC in VMware one of the foundational elements of modern data center virtualization.
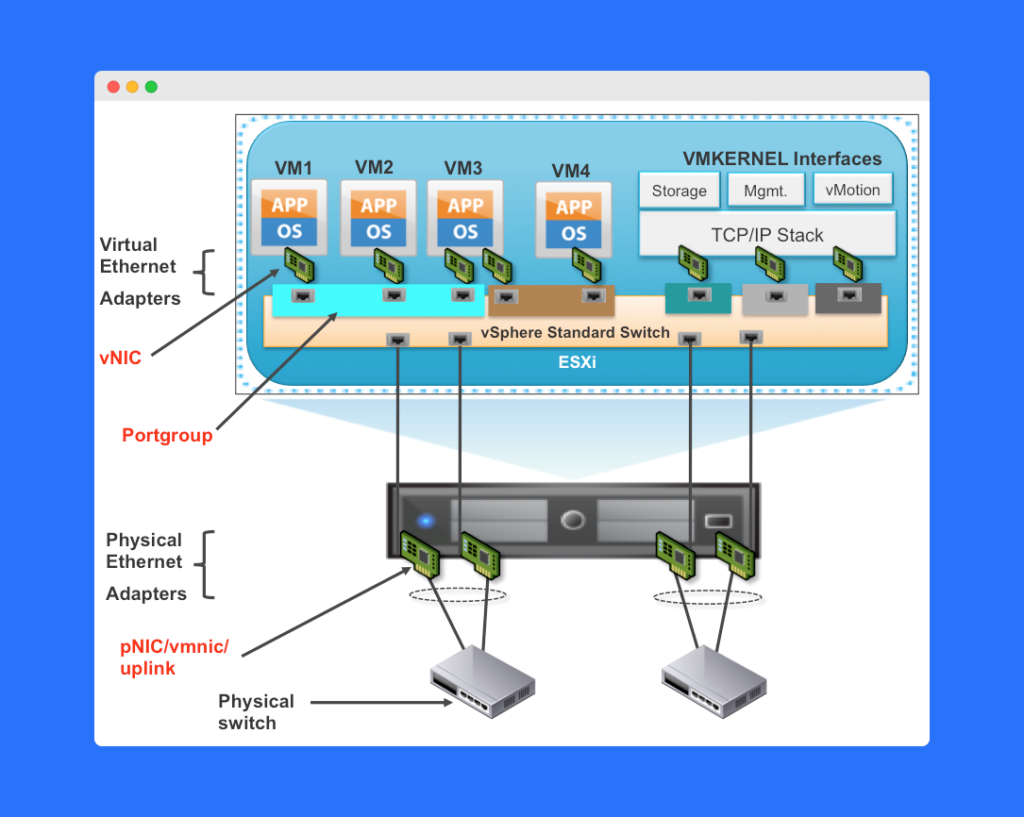
How Does a vNIC Work?
To understand how a vNIC in VMware works, it helps to compare it with a physical NIC.
A physical NIC is a hardware device that sends and receives packets through a network switch. Similarly, a vNIC operates within the virtual layer:
- The vNIC receives incoming packets on the host.
- It forwards them to another vNIC or external network via the vSwitch.
- The vSwitch determines where the packet should go — either to another VM, a different host, or a physical network.
VMware uses MAC addresses, VLAN IDs, and QoS (Quality of Service) settings to ensure that data is efficiently and securely transmitted between endpoints.
Key Features and Configuration of vNICs
You can configure a vNIC in VMware using the vSphere Client, VMware’s graphical interface for managing virtual environments. Administrators can adjust several key network settings for each vNIC:
- MAC Address – Unique identifier for each vNIC to manage data flow.
- VLAN ID – Segments network traffic for improved organization and security.
- Network Bandwidth – Controls throughput to ensure balanced resource use.
- Port Group Assignment – Connects the vNIC to a specific Virtual Port Group (VPG) for consistent policy application.
Benefits of Using a vNIC in VMware
Using vNICs in a virtualized environment provides significant flexibility, security, and performance advantages:
Flexibility
vNICs allow you to scale and manage virtual networks with ease. You can add or remove vNICs, adjust VLANs, or apply new network policies quickly — all without hardware changes.
Efficiency
A vNIC in VMware enables efficient communication between VMs and physical networks. This reduces network management overhead and improves overall performance in large environments.
Enhanced Security
vNICs can be configured with Access Control Lists (ACLs) and other security settings to limit unauthorized access and isolate sensitive workloads.
Quality of Service (QoS)
QoS policies ensure critical applications get priority network bandwidth, maintaining stability even under high workloads.
vNICs and Virtual Port Groups (VPGs)
A Virtual Port Group (VPG) is a logical grouping of vNICs that share the same networking properties.
When you assign a vNIC to a VPG, all VMs connected to that group inherit the same network settings, such as VLAN ID, security, and traffic shaping policies.
This approach simplifies network management, especially in large-scale VMware environments where dozens or even hundreds of VMs need consistent network configurations.
Integration with Physical Networks
While vNICs handle internal communication within a host, they can also connect to external physical networks.
VMware achieves this through technologies such as:
- VXLAN (Virtual Extensible LAN) – Enables network overlays to connect VMs across different physical locations.
- NAT (Network Address Translation) – Allows VMs to access external networks securely without exposing internal IP addresses.
This hybrid connectivity allows VMs to access internet resources, corporate networks, or cloud environments without compromising security.
Best Practices for Managing vNICs in VMware
To get the most out of your vNIC configurations, follow these best practices:
- Use descriptive names for vNICs and VPGs (e.g., “Prod_Network,” “Test_Lab”).
- Regularly review MAC address assignments to avoid conflicts.
- Apply VLAN tagging for better traffic segmentation.
- Monitor network utilization and adjust QoS settings as needed.
- Keep vSphere tools up-to-date for maximum compatibility and security.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A vNIC in VMware is a virtual network interface card that allows virtual machines to communicate with each other and physical networks.
A physical NIC is hardware-based, while a vNIC is software-based and exists within a virtualization platform like VMware vSphere.
A vNIC connects to a vSwitch and may be assigned to a Virtual Port Group (VPG), which defines its network policies and VLAN settings.
vNICs offer flexibility, efficiency, enhanced security, and QoS controls, making them ideal for managing large-scale virtual environments.
Yes, through vSwitch uplinks, VXLAN, or NAT, vNICs can connect to external networks like corporate or internet environments.
Conclusion
A vNIC in VMware is an essential component for managing communication between virtual and physical networks. By using virtual NICs, organizations can simplify network management, improve flexibility, and enhance security — all while reducing reliance on physical hardware.
Whether you’re managing a small lab or a large enterprise data center, understanding how vNICs work helps you design efficient and scalable virtual network infrastructures.





