Kubernetes relies on several control plane components to ensure smooth cluster operations. Among these, CoreDNS plays a vital role in DNS-based service discovery and name resolution within a Kubernetes environment. In this guide, we’ll explore what CoreDNS is, why it’s important, and how it works in Kubernetes clusters.
Table of Contents
What is CoreDNS in Kubernetes?
CoreDNS is the default DNS server used in Kubernetes clusters. It ensures that services and pods can communicate with each other seamlessly using domain names instead of IP addresses.
Key features of CoreDNS include:
- Default Name Server: CoreDNS is automatically deployed as the default DNS server in Kubernetes.
- Flexible and Lightweight: Written in Go, it provides high performance and flexibility.
- Deployment in kube-system Namespace: It runs as a Kubernetes Deployment inside the
kube-systemnamespace. - Cluster DNS Service: Exposed via a
ClusterIPservice under the namekube-dns.
Why Do We Need CoreDNS in Kubernetes?
CoreDNS provides essential DNS resolution functionalities that simplify communication within Kubernetes clusters. Some key use cases include:
- Service Discovery
- Translates service names such as
myservice.default.svc.cluster.localinto corresponding cluster IPs.
- Translates service names such as
- Pod DNS Resolution
- Resolves pod hostnames (if configured), enabling pod-to-pod communication via DNS.
- External DNS Resolution
- Forwards unknown queries to upstream DNS servers, allowing pods to access external domains.
- Custom DNS Rules
- Lets cluster administrators define custom domain mappings and tailor DNS behavior as needed.
How Does CoreDNS Work in Kubernetes?
The working of CoreDNS follows a step-by-step process for resolving DNS queries inside a cluster:
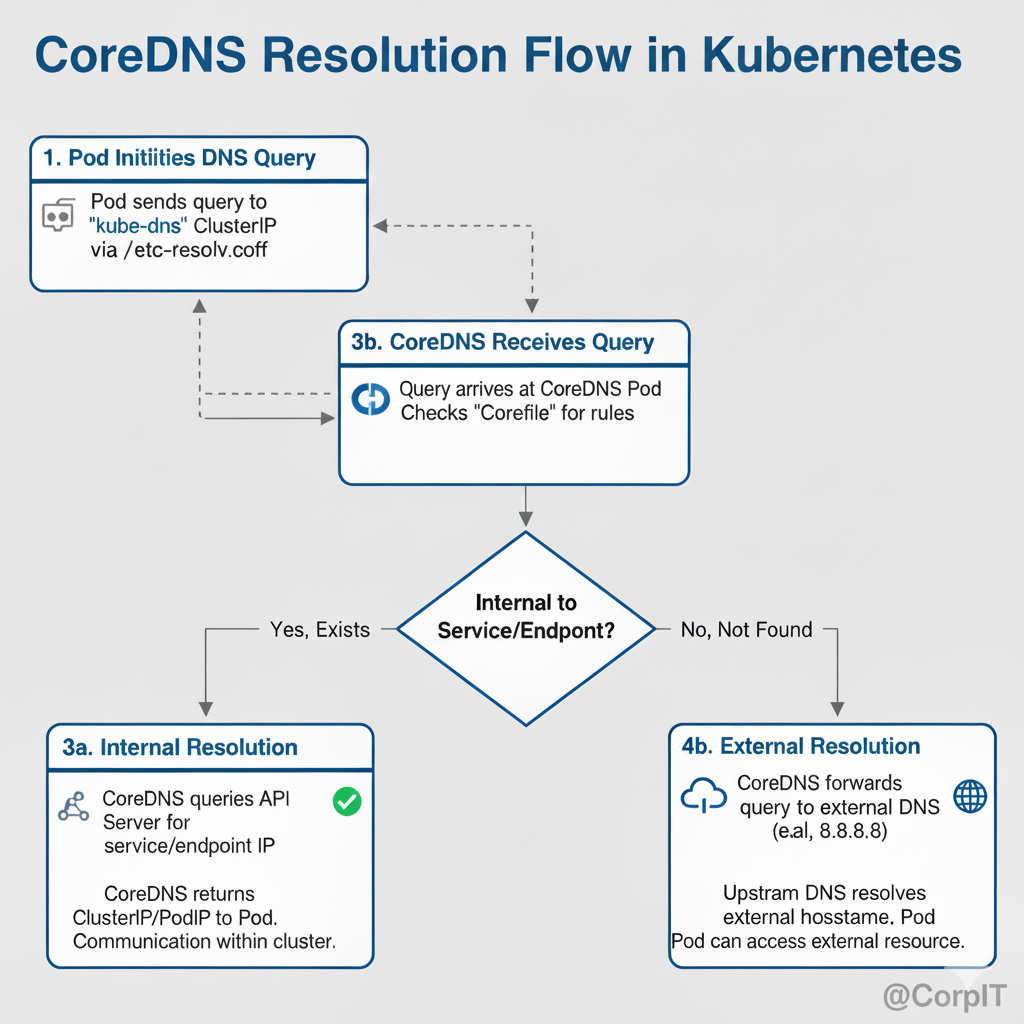
- Pod Makes a DNS Query
- When a pod needs to resolve a hostname, it sends a query via
/etc/resolv.conf, which points to thekube-dnsClusterIP.
- When a pod needs to resolve a hostname, it sends a query via
- CoreDNS Receives the Query
- CoreDNS checks how to handle the request based on its configuration.
- Kubernetes API Server Lookup
- CoreDNS communicates with the Kubernetes API Server to determine if the queried service or endpoint exists.
- Response Handling
- If the service exists, CoreDNS returns the corresponding cluster IP (or pod IP).
- If it does not exist, CoreDNS forwards the query to an upstream DNS for external resolution.
This mechanism ensures smooth service-to-service communication and external domain resolution within Kubernetes clusters.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
CoreDNS acts as the default DNS server, enabling service discovery and DNS resolution for pods and services in a cluster.
Yes, CoreDNS forwards unknown queries to upstream DNS servers, allowing pods to access the internet.
CoreDNS is deployed as a Deployment in the kube-system namespace and exposed via the kube-dns service.
Yes, administrators can customize CoreDNS behavior using a Corefile configuration file to define custom DNS rules.
CoreDNS replaced the older kube-dns component and became the default DNS service starting from Kubernetes v1.13.
kubectl get pods -n kube-system -l k8s-app=kube-dns
This command will show the running CoreDNS pods.
[Video] Explained CoreDNS in Kubernetes
Conclusion
CoreDNS in Kubernetes is a powerful and flexible DNS solution that ensures smooth service discovery, pod DNS resolution, and external domain access. By integrating tightly with the Kubernetes API, CoreDNS makes networking inside the cluster both reliable and efficient.
For a deeper dive into Kubernetes DNS architecture, check the official Kubernetes documentation.





